Today we explore the differences between Geotargeting vs Geofencing, which are both forms of location-based targeting but have different goals.
Location-based marketing has been around for a long time, even before the advent of the Internet. The way it was done back then differed from how it is done now.
Examples of early location-based marketing include a girl giving out coupons in Paris to promote a nearby boutique or a flyer left on your doorstep announcing the opening of a new Mexican restaurant in the area.
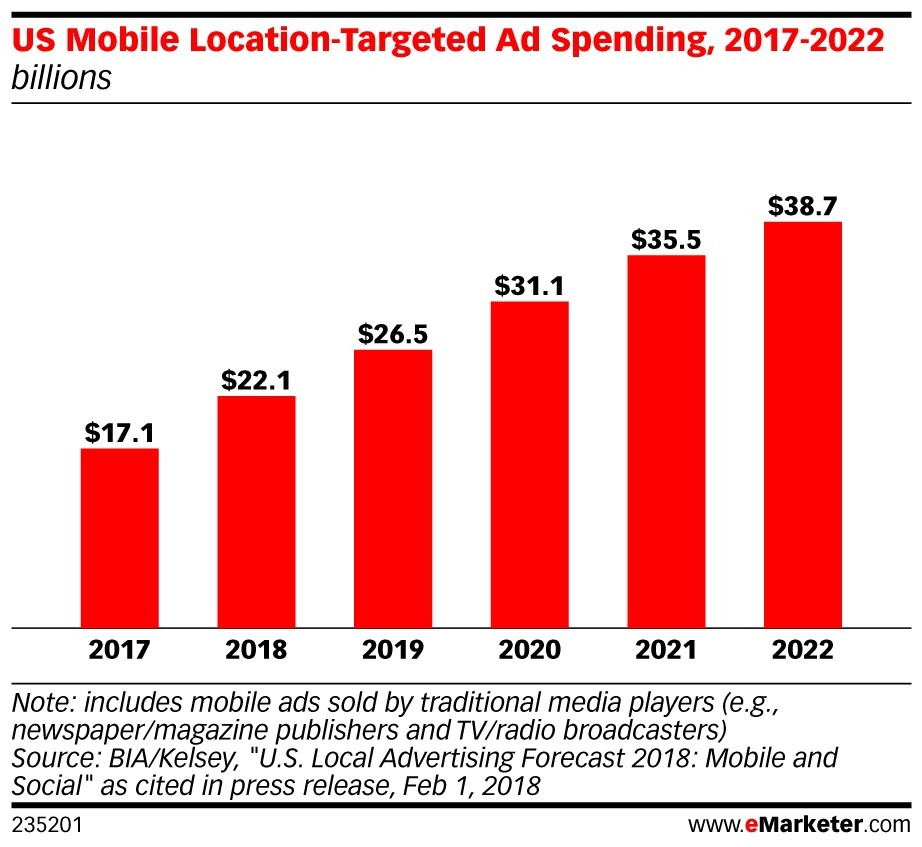
Over time, with the assistance of various modern services, agencies, and software, the location-based marketing industry has grown significantly and is now valued at $5.6 billion.
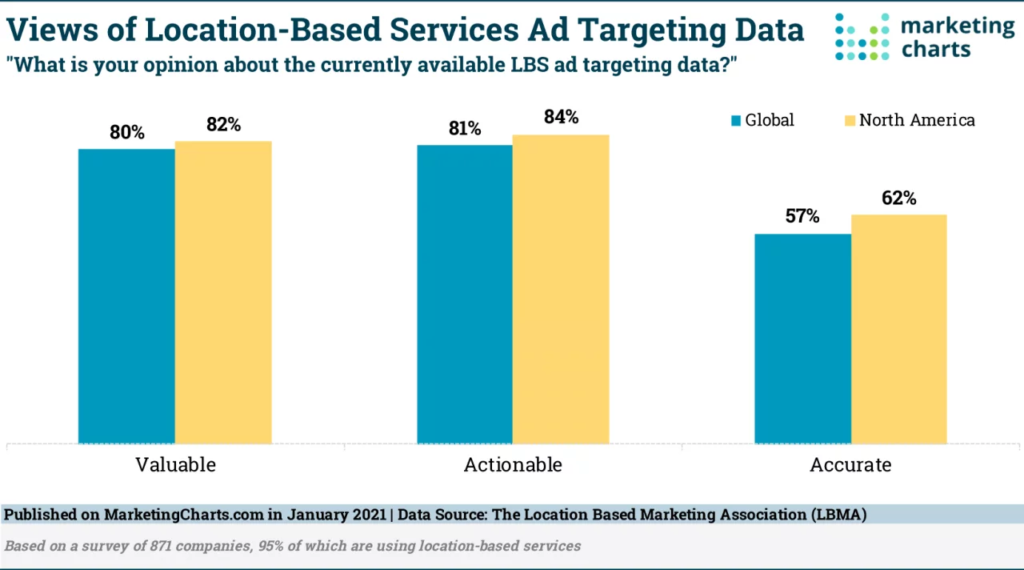
Location-based advertising has become a popular strategy for marketers, with 9 out of 10 reporting positive results.
This approach, which is both simple and traditional, has proven to be highly effective in the current market.
In today’s highly competitive global economy, businesses must know all possible strategies to give them an edge over their rivals.
The statistics back up the effectiveness of location-based advertising, with studies showing that it can be up to 20 times more effective than simply displaying banner ads without any location-based filtering.
Given these impressive results, it’s definitely worth considering implementing location-based advertising in your marketing strategy to see if it can work wonders for your business.
Key Points Covered in the Article
- The Importance of Location-Based Marketing in Advertising.
- Different Types of Location-Based Marketing Strategies.
- Understanding Geotargeting: How Does It Work?
- Understanding Geofencing: How Does It Work?
- Comparing Geotargeting and Geofencing: Differences and Similarities.
- Tips and Best Practices for Successful Location-Based Marketing.
How Location-Based Marketing Helps a Business?
Location-based marketing has become a crucial aspect of advertising in today’s market. With great tools and services available, businesses can strategize their location-based marketing effectively and stay ahead of their competition.
Implementing location-based advertising offers a range of benefits that can help businesses drive revenue growth.
- Location-based advertising can result in higher click-through rates.
- Location-targeted ads are more relevant and effective in converting clients, resulting in a better return on investment.
- Focusing on the client’s needs can help businesses create a better user experience, leading to a loyal customer base and improved brand image.
- Location-based marketing can help businesses raise the quality of sponsors.
- Highlighting the advertiser being endorsed can shift the focus away from the competition and create a better relationship with sponsors.
- Location-based advertising focuses on where and when impacting the return on investment and driving higher revenue growth.
- During quiet periods, location-based advertising can effectively leverage businesses to drive up their revenue.
- By utilizing the plethora of tools and services available, businesses can stay ahead of the competition and drive higher click-through rates, create a better user experience, raise the quality of their sponsors, and reach out to their audience at the right time.
Types of Location-Based Marketing
Location-based marketing has undergone significant developments in recent years; it takes various forms today.
Marketers use five commonly used approaches to location-based advertising to create better strategies.
- Geotargeting: Geotargeting is one approach that identifies the user’s location via their IP address and then delivers relevant, personalised messages. For example, an app with access to a user’s location might notify them of an offer at a nearby store.
- Geo Conquesting: Another approach is Geo Conquesting, which aims to attract customers away from a competitor and towards a particular business. This is achieved by sending customers a better offer as they cross a marked boundary using their location data.
- Geofencing: Geofencing is the creation of a virtual boundary around a specific location. When a user crosses this boundary, it triggers an action, such as an advertising campaign aimed at that user.
- Mobile targeting: Mobile targeting uses both geotargeting and geofencing to deliver ads to users’ mobile devices based on their location data and when they are close to the advertised store.
- Beaconing: Beaconing involves installing beacons that use Bluetooth or Wi-Fi to send signals to mobile devices. When a phone with an installed application enters a designated area, the beacon identifies the device and sends relevant marketing messages to it.
These five approaches to location-based advertising provide businesses with different ways to reach out to their customers and increase engagement.
By utilizing these tools, businesses can create more effective advertising campaigns, deliver better user experiences, and ultimately drive higher revenue growth.
How Does Geotargeting Work?
Geotargeting is a marketing strategy that uses the geographic location of a user to display ads. It can be applied on a country, city, district or region level.
Geotargeting is not only beneficial for advertising but also helps the public in various ways.
For instance, if someone is searching for a place to eat while visiting a new area, they can easily search for “restaurants near me” to find the nearest options.
Geotargeting can be categorized into three types: local targeting, hyper-local targeting, and advanced geographic targeting.
In local targeting, ads are displayed within a specific region or area.
Hyper-local targeting, on the other hand, is when a specific location is chosen, such as within 1000 meters of a store, and ads are displayed accordingly.
Advanced geographic targeting, meanwhile, targets users searching for a specific location, regardless of their current geographic location.
How Does Geofencing Work?
Geofencing is a location-based advertising concept that relies on various tools and services such as Wi-Fi, cellular data, RFID, and more to create a specific boundary around a particular area when a user’s device enters or searches up the set location, brochures, coupons, notifications, text messages, emails, and other forms of advertising become active.
It’s worth noting that geofencing isn’t limited to just marketing. It’s a concept that has relevance in other fields, such as aviation, logistics, and smart home control.
The ability to create a virtual boundary around a physical location has a wide range of applications beyond just advertising.
Geotargeting vs. Geofencing
Geotargeting and Geofencing are two commonly used marketing strategies, but they have some significant differences that businesses should be aware of. Here is a breakdown of the two:
| GEOTARGETING | GEOFENCING |
|---|---|
| Raises brand awareness and secures future conversions | Offers an Uber-relevant advertising experience to potential leads for quick conversion |
| Sets a broad geographic boundary based on city, country or town | Sets a narrow and more focused area by setting a fence around a specific geographic location |
| Advertises in a hyper-personalized manner by combining with other filters | Sends notifications to anyone who enters said parameter or searches for the location |
| Does not store user’s location data | Collects and stores user’s location data and history |
| Used by almost every kind of business | Used specifically by event agencies, advertisers, and business owners |
| Depends on a user’s IP address | Leverages GPS, Wi-Fi, cellular data, and more |
Conclusion
In conclusion, location-based marketing has evolved significantly over the years, offering several approaches for marketers to strategize better. Geotargeting and geofencing are two approaches advertisers and publishers commonly use for location-based advertising.
While geotargeting works by leveraging a user’s IP address and sending them personalized notifications, geofencing creates a specific perimeter around a location and sends notifications to anyone who enters it.
Geofencing collects a user’s location data and stores their location history, whereas geotargeting does not store such data. Additionally, geotargeting is usually combined with other filters for hyper-personalized advertising, whereas geofencing is used specifically by event agencies, advertisers, and business owners.
Geotargeting is used by almost every type of business while geofencing leverages GPS, Wi-Fi, cellular data, and other tools and services to create a much narrower and more focused area for advertising.
Overall, geotargeting and geofencing have unique advantages and can be used in different ways depending on the business’s specific needs. Location-based marketing is a powerful tool that can help businesses increase brand awareness, secure future conversions, and provide potential leads with a more relevant advertising experience.
Geotargeting vs Geofencing – FAQs
Q: Why Use Geofencing for Advertising?
ANS: Geofencing and other forms of location-based marketing have several benefits. One key advantage is the ability to allocate your marketing budget more effectively by targeting users in specific geographic locations.
Geofencing can also help increase sales by providing hyper-relevant advertising to potential customers in the right place at the right time. This, in turn, can enhance user experience and lead to higher conversion rates.
Q: What are Some Good Practices for Location-Based Marketing?
ANS: Several best practices for location-based marketing include using relevant geotargeting or geofencing platforms. You can also identify the locations your users frequent and target your advertising efforts accordingly.
Creating location-based landing pages, using geo-conquesting to target your competitor’s locations, and leveraging data analytics to optimize your campaigns are also effective strategies.
Q: Is Geofencing Accurate?
ANS: Geofencing is highly accurate due to the combination of GPS, Wi-Fi, cellular data, and other services it uses to determine a user’s location. Even in rural areas where services may be limited, geofencing accuracy can still reach within a few hundred meters.
This level of precision is crucial for effective location-based advertising, ensuring that your messages are delivered to the right audience at the right time.


